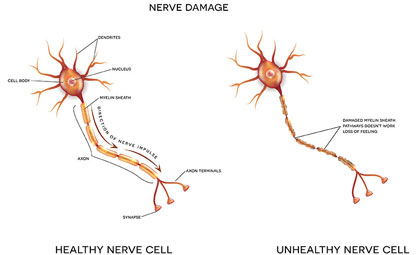
Arthritis and neurological disorders can both contribute to nerve damage of the peripheral nerves, a condition referred to as peripheral neuropathy. The damage can lead to decreased or abnormal sensations.
What are the symptoms of Peripheral Neuropathy?
One of the first symptoms is numbness in the toes. Shooting or stabbing pain in the toes is also possible. Many patients report a pins and needles sensation. Other symptoms may include:
- Gradual onset of numbness, prickling or tingling in your feet or hands, which can spread upward into your legs and arms
- Sharp, jabbing, throbbing, freezing or burning pain
- Extreme sensitivity to touch
- Lack of coordination and falling
- Muscle weakness or paralysis if motor nerves are affected
Diagnosis
The following tests may be used to determine if peripheral neuropathy is present:
- Nerve conduction velocity (NCV) tests can measure the degree of damage in large nerve fibers, revealing whether symptoms are caused by degeneration of the myelin sheath or the axon. During this test, a nerve fiber responds by generating its own electrical impulse when it a probe electrically stimulates it.
- Electromyography (EMG) involves inserting a fine needle into a muscle to record electrical activity when muscles are at rest and when they contract. EMG tests can help differentiate between nerve and muscle disorders, and also helps differentiate abnormal electrical activity.
- Nerve biopsy involves removing and examining a sample of nerve tissue, most often from the lower leg. This is an invasive procedure that is difficult to perform and may cause neuropathic side effects.
- Skin biopsy is a test in which doctors remove a thin skin sample and examine nerve fiber endings. This test offers some unique advantages over NCV tests and nerve biopsy.
How is it treated?
Seeking treatment is very important. Without treatment, more serious issues can develop. Regular exercise can help to improve blood flow and your doctor may recommend ointments and medication to reduce inflammation and pain.
Massage, physical therapy, and electrical nerve stimulation can all help to improve nerve function.
Since peripheral neuropathy is most common among diabetics, inspecting feet regularly and monitoring blood sugar levels is an important part of managing symptoms and preventing further damage.