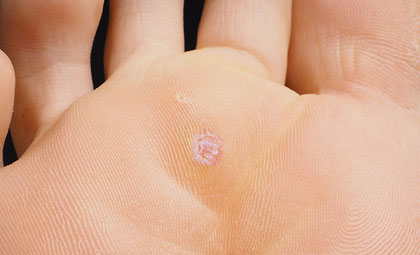

Warts are caused by infections that enter your skin through small cuts and are characterized by rough growths on the skin’s surface. Patients who spend a lot of time barefoot in common areas, such as locker rooms or showers, are at an increased risk for developing plantar warts, which are located on the feet. Warts are contagious, and be spread by contact. Even though most do disappear spontaneously, it may take years for warts to disappear.
What are the symptoms of Warts?
They are often an inch or more in size. They can be spongy and red, black, or brown. They often reoccur in the same areas and can also develop in clusters. They most commonly grow on the fingers, nails, and back of hands. Broken skin is also a common area for warts to grow, such as picked hangnails and fingernails that have been bitten.
How are they treated?
They can spread to other areas very quickly, so early treatment is necessary. Your doctor may remove the wart with a small instrument. Warts, most commonly with children, often go away without treatment. For adults, though, they do not disappear as quickly. For warts that do not disappear after a long period of time or hurt, there are several treatments that can be made which include:
- Cantharidin: A dermatologist may treat a wart in the office by “painting” it.. Cantharidin causes a blister to form under the wart. In a week or so, you can return to the office and the dermatologist will clip away the dead wart.
- Cryotherapy: Most common for adults and older children, cryotherapy is the most common treatment, where they freeze the wart. The treatment is not painful, but may need to be repeated.
- Curettage: Curettage involves scraping off (curetting) the wart with a sharp knife or small, spoon-shaped tool. These two procedures often are used together.
- Excision: The doctor cuts out the wart.